20+ Best Neo4j Interview Questions And Answers

Neo4j is a popular open-source graph database management system that is widely used for storing and querying data represented as graphs.
In this article, we are going to list the frequently asked questions and answers in the Neo4j interviews. We hope these Neo4j interview questions will help you in your interview.
Here are some common Neo4j Interview Questions:
1. What is a graph database?
A graph database is a database management system that is designed to store, retrieve, and manage data that is represented as a graph.
In a graph database, data is stored as nodes (vertices) and relationships (edges) that connect the nodes. Graph databases are well-suited for storing complex and interconnected data and for querying data in a flexible and efficient manner.
2. What is a node in Neo4j?
In Neo4j, a node is a fundamental data unit that represents an entity in the graph. It can store any number of key-value pairs, called properties, that describe the entity and its characteristics. A node is connected to other nodes in the graph through relationships, which represent the connections or relationships between the entities.
For example, in a social network, a node might represent a person and have properties such as “name,” “age,” and “location.” The node might also be connected to other nodes that represent the person’s friends, family, or coworkers, through relationships that represent the nature of the connection (e.g., “friend,” “parent,” or “colleague”).
Nodes are an important part of Neo4j and are used to model and represent the data in a graph database. They allow you to create a flexible and expressive model of your data and make it easy to query and manipulate the data using the Cypher query language.
3. What is a relationship in Neo4j?
In Neo4j, a relationship is a data unit that represents a connection or relationship between two nodes in the graph. Relationships are directed, which means that they have a start node and an end node, and they always have a specific type that describes the nature of the relationship.
For example, in a social network, a relationship might connect two nodes that represent people, with a type of “friend.” The relationship would have a start node that represents the person initiating the friendship and an end node that represents the person accepting the friendship.
Relationships are an important part of Neo4j and are used to model and represent the connections and relationships between entities in the graph. They allow you to capture the structure and context of your data and make it easy to query and manipulate the data using the Cypher query language. Relationships can also have properties, which are key-value pairs that describe the relationship in more detail.
4. How to create a node in Neo4j?
To create a node in Neo4j, you can use the CREATE clause in the Cypher query language.
The basic syntax for creating a node is:
|
|
Here, node is a placeholder for the node you want to create, Label is the label you want to assign to the node (optional), and properties are the key-value pairs you want to assign to the node as properties.
For example, to create a node that represents a person with the properties “name” and “age,” you could use the following query:
|
|
This would create a node with the label “Person” and the properties “name” and “age.” You can then use this node in subsequent queries to connect it to other nodes or to perform operations on it.
It’s also possible to create multiple nodes in a single query by separating them with a comma, like this:
|
|
This would create two nodes with the label “Person” and the specified properties.
5. How to create a relationship in Neo4j?
To create a relationship in Neo4j, you can use the CREATE clause in the Cypher query language.
The basic syntax for creating a relationship is:
|
|
Here, startNode is the node at the start of the relationship, relationship is a placeholder for the relationship you want to create, REL_TYPE is the type of relationship, and endNode is the node at the end of the relationship.
For example, to create a relationship that represents a friendship between two people, you could use the following query:
|
|
This would create a relationship of type “FRIEND” between the two nodes p1 and p2, with p1 as the start node and p2 as the end node.
It’s also possible to create multiple relationships in a single query by separating them with a comma, like this:
|
|
This would create two relationships: one of type “FRIEND” between p1 and p2, and one of type “FOLLOWS” between p1 and p3.
You can also specify properties for the relationship by adding a {properties} map after the relationship type, like this:
|
|
This would create a relationship of type “FRIEND” between p1 and p2, with the property “since” set to the value “2022-01-01”.
6. What is Neo4j used for?
Neo4j is used for a wide variety of applications, including data modeling, data management, real-time analytics, and recommendation engines. It is particularly well-suited for applications that involve complex, interconnected data and require fast query performance.
7. How do you query data in Neo4j?
Neo4j uses a query language called Cypher to query data stored in the database. Cypher is a declarative language that uses a simple and intuitive syntax to describe patterns in data and to specify the relationships between data elements. Read more about Cypher Query Language here.
8. How do you import data into Neo4j?
There are several ways to import data into Neo4j, including:
- Using the
LOAD CSVclause in a Cypher query to import data from a CSV file - Using the Neo4j Import Tool to import data from CSV, JSON, or other formats
- Using the Neo4j ETL tool to import data from a variety of sources, including other databases, web APIs, and message queues
9. Can Neo4j be used with other programming languages?
Yes, Neo4j can be used with a variety of programming languages, including Java, Python, and JavaScript. It provides a number of official drivers and integrations that make it easy to use Neo4j with these languages. In addition, there are many third-party libraries and tools that support Neo4j integration with other languages.
10. What is the Neo4j Graph Platform?
The Neo4j Graph Platform is a collection of tools and technologies that enable organizations to build, deploy, and manage graph-powered applications and solutions at scale. The platform includes the Neo4j graph database, a variety of data integration and visualization tools, and a range of enterprise-grade features and support options.
11. How is Neo4j different from a traditional relational database?
Neo4j is different from traditional relational databases in several ways:
- Structure: A traditional relational database stores data in tables with rows and columns, while a graph database stores data as nodes and relationships. This makes it easier to represent complex and interconnected data in a graph database.
- Query language: A traditional relational database uses Structured Query Language (SQL) to query data, while Neo4j uses Cypher. Cypher is specifically designed for querying graph data and is more expressive and intuitive than SQL for this purpose.
- Performance: Graph databases are typically faster than traditional relational databases for querying data that is connected in complex ways. This is because they can use the relationships between data elements to efficiently navigate the graph, rather than having to perform expensive join operations.
12. How does Neo4j scale?
Neo4j is designed to scale horizontally, which means that it can distribute data and workloads across multiple machines in a cluster. This allows Neo4j to handle larger volumes of data and higher levels of concurrency without sacrificing performance.
Neo4j also provides a number of features and options to support horizontal scaling, including:
- Sharding: Data can be divided into shards and distributed across the cluster to improve the read and write performance.
- Replication: Data can be replicated across the cluster to improve availability and reduce the risk of data loss.
- Load balancing: Queries and transactions can be automatically routed to the appropriate machine in the cluster to improve performance.
13. Is Neo4j open source?
Yes, Neo4j is open-source software that is available under the GNU General Public License (GPLv3). This means that the Neo4j source code is freely available and can be modified and distributed by anyone.
Neo4j also offers a commercial edition that includes additional features and support options.
14. What is a graph data model?
A graph data model is a way of representing data as a graph, with nodes representing entities (such as people, products, or events) and relationships representing the connections or interactions between those entities. In Neo4j, a graph data model is defined using a property graph model, which consists of nodes, relationships, and properties.
15. How do you create a graph data model in Neo4j?
To create a graph data model in Neo4j, you can use the Cypher query language to create nodes and relationships and to specify the properties of those nodes and relationships. You can also use the Neo4j Browser, a graphical tool for interacting with the database, to create and modify the graph data model.
16. How do you visualize a graph in Neo4j?
There are several tools and techniques for visualizing a graph in Neo4j, including:
- Neo4j Browser: The Neo4j Browser includes a visualizer that allows you to view and explore the graph data stored in the database.
- Graph visualization libraries: There are many open-source libraries, such as D3.js and Gephi, that can be used to visualize graph data from Neo4j.
- Graph visualization tools: There are also a number of specialized tools, such as Linkurious and KeyLines, that are designed specifically for visualizing graph data and that can be used with Neo4j.
17. What are some common use cases for Neo4j?
Some common use cases for Neo4j include:
- Social network analysis
- Fraud detection
- Recommendation engines
- Network and IT operations
- Supply chain management
- Master data management
- Cybersecurity
18. What are some other popular graph databases?
Some other popular graph databases include:
- Microsoft Azure Cosmos DB
- Amazon Neptune
- Virtuoso
- OrientDB
- TigerGraph
- DGraph
- Fauna
- TinkerGraph
- GraphDB
- FlockDB
- ArangoDB
- JanusGraph
- Stardog
- AllegroGraph
- MemGraph
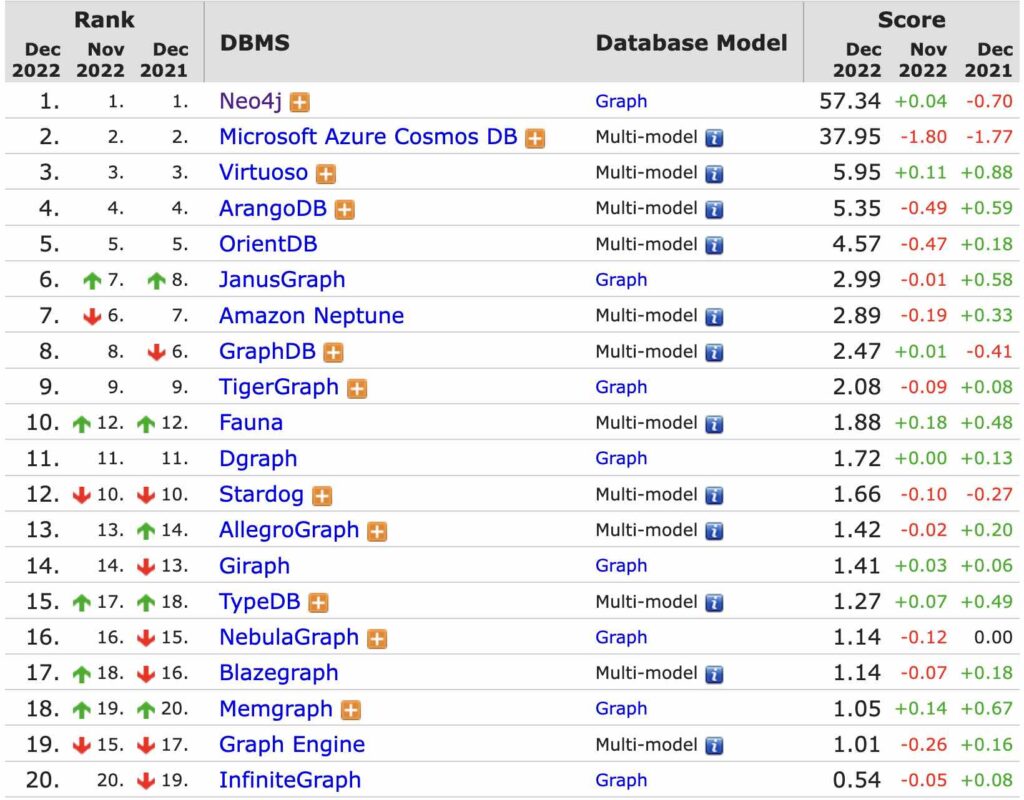
Here is the list of the top graph databases as per DB-Engines:
19. What is the Neo4j Graph Algorithms library?
The Neo4j Graph Algorithms library is a collection of graph algorithms that can be used with Neo4j to solve common problems, such as finding the shortest path between two nodes or identifying communities within a graph. The library includes more than 50 algorithms and is implemented in Java and accessible through the Neo4j API.
20. How do you secure a Neo4j database?
There are several ways to secure a Neo4j database, including:
- Enabling authentication and authorization: Neo4j supports various authentication mechanisms, such as basic auth and LDAP, and allows you to control access to the database by assigning roles to users.
- Encrypting data at rest: Neo4j supports data encryption at rest using the AES-256 cipher.
- Encrypting data in transit: Neo4j supports encrypted connections using TLS (Transport Layer Security).
- Implementing security best practices: It is important to follow security best practices, such as applying software updates and patches, keeping the database and operating system up to date, and implementing network security measures.
21. How do you troubleshoot Neo4j issues?
If you are experiencing issues with your Neo4j database, there are several steps you can take to troubleshoot the problem:
- Check the Neo4j logs: The Neo4j logs can provide valuable information about errors, warnings, and other events that may be related to the issue.
- Use the Neo4j Browser to run queries and inspect the data: The Neo4j Browser can be used to run Cypher queries and inspect the data stored in the database, which may help to identify the cause of the issue.
- Consult the Neo4j documentation: The Neo4j documentation contains detailed information about the database and its various features and options, as well as troubleshooting guidance.
- Seek help from the Neo4j community: If you are unable to resolve the issue on your own, you can seek help from the Neo4j community, which includes a large and active user base that may be able to offer assistance and support.
22. What are some best practices for working with Neo4j?
Here are some best practices for working with Neo4j:
- Use the appropriate data model: Choose the right data model for your use case. If your data is highly interconnected and you need to traverse the graph efficiently, a graph database like Neo4j may be a good choice. If your data is primarily tabular, a traditional relational database may be a better fit.
- Use appropriate data types: Use the appropriate data types for your data. For example, use the
Datedata type to store dates and theNumberdata type to store numbers. This will make it easier to query and manipulate the data. - Use indexes wisely: Use indexes to improve query performance, but be aware that adding too many indexes can negatively impact write performance.
- Monitor and optimize performance: Use tools like the Neo4j Browser and the Neo4j Profiler to monitor and optimize the performance of your database.
- Use transactions appropriately: Use transactions to ensure the consistency and isolation of your data, but be aware that overusing transactions can impact performance.
- Use high-quality data: Ensure that your data is accurate, complete, and up to date. This will make it easier to get meaningful results from your queries.
23. What are some common pitfalls to avoid when working with Neo4j?
Here are some common pitfalls to avoid when working with Neo4j:
- Choosing the wrong data model: If your data is not well-suited for a graph data model, you may struggle to get the results you want from your queries.
- Overloading the database: If you try to store too much data in a single Neo4j database, you may run into performance issues. It may be necessary to scale horizontally or to partition the data across multiple databases.
- Neglecting data quality: If your data is dirty or incomplete, you may get incorrect or misleading results from your queries.
- Not optimizing queries: If you write inefficient Cypher queries, you may experience poor performance. Be sure to use appropriate indexes and tune your queries for optimal performance.
- Ignoring security: Neglecting security best practices can leave your Neo4j database vulnerable to attacks. Be sure to enable authentication, encrypt data at rest and in transit, and follow other security best practices.
We hope these Neo4j interview questions and answers help you in your next Neo4j interview. Please provide your feedback.